Customer Segmentation Strategy: 7 Methods Every B2C Marketer Must Know
84% of consumers prefer companies that provide a personalized experience.
If consumers desire personalized experiences, why would a brand use a one-size-fits-all approach for its audience? More importantly, how can your brand deliver such tailored experiences?
The answer lies in your customer segmentation strategy.
With customer segmentation, you can target your ads and messaging to the most relevant audience. That way, you’d spend your time and money on marketing that works and helps you achieve your business goals.
In this article, we’ll dive into seven marketing segmentation strategies and best practices to follow when developing a customer segmentation strategy. We’ll also cover how to choose from customer segmentation models for your brand.
What is a Customer Segmentation Strategy?
A customer segmentation strategy is a roadmap for identifying who your customers are, categorizing your customer base into distinct groups based on their unique characteristics, and delivering each group with the most relevant message.
Your strategy covers which customer segmentation model you’ll use to group customers (by age, location, spending habits, interests, etc.), what data you’ll use to create these distinct groups, how you’ll market to each group differently, and what goals you want to achieve—like more sales, better customer loyalty, or higher customer engagement.
For example, a shoe company might split its customer base into three groups: athletes, casual wearers, and fashion lovers.
They’d look at what customers had bought before and ask them questions to determine which group they belonged to.
Then they’d send different emails to each group. Athletes get emails about how the shoes help them perform better. Casual wearers get emails about comfort. Fashion lovers get emails about the latest styles.
You get the gist.
That’s what a customer segmentation strategy looks like in action.
What is a Customer Segmentation Model?
A customer segmentation model is a framework used to divide your audience base into smaller groups or segments, based on common behaviors and characteristics. This helps target your audience more accurately, to better personalize your messages, and ultimately enhance the customer experience.
Essentially, a segmentation model tells you how to segment your customers, using different types of customer segmentation. It lays out:
- What criteria you’ll use to group customers (age, psychographics, behavior, and so on)
- Why you’ll segment customers (awareness, retention, loyalty, etc.)
- Which sources of customer data you’ll rely on
It ensures you’re segmenting customers in a way that’s relevant to your brand’s goals. You should also be able to measure the performance of each segment.
Remember, the objective of using a segmentation model is to tailor your messaging to each segment, so that it resonates with them.
7 Winning Marketing Segmentation Strategies and Methods
Effective segmentation helps you stop treating every customer the same and start delivering experiences that actually resonate.
Here are some customer segmentation strategies or models you can use.
1. Demographic segmentation

Source: https://eathungryroot.com/hungryroot/goodbye-meal-kits-smart-account
Demographic segmentation is a common customer segmentation model that categorizes customers based on personal characteristics such as age, income, gender, education, or family status.
A meal planning app might segment users into three main demographic groups: young professionals (25-35, higher income, time-poor), families (35-50, middle income, cooking for multiple people), and retirees (60+, fixed income, cooking for one or two).
Each segment gets different marketing messages. Young professionals see quick 15-minute recipes. Families see budget-friendly meal prep for four. Retirees see simple, heart-healthy meals with minimal waste.
This customer segmentation strategy is effective because the demographic directly influences customer needs and shopping behavior. A 28-year-old living alone shops differently from a 45-year-old feeding three kids. The data points are easily collected from your target audience, allowing for an accurate prediction of customer behavior.
How to do it
Your signup form should collect age and basic demographic information about your customers.
Data can come from your website, social media interactions, and general sales. Customer engagement technology like MoEngage allows you to set up surveys on your website or in-app surveys to collect vital data.
Think about how your features align with specific demographics. List which offerings make sense for college students versus retirees. Which products fit high earners versus budget-conscious shoppers? A simple spreadsheet matching demographics to product features works well here.
Focus on 3-5 segments that matter to your brand. Segmenting by every possible variable dilutes your efforts. Instead, zero in on factors that affect how customers use your product in your market.
Separate customer onboarding flows for each segment can dramatically improve the customer experience. When a 30-year-old signs up for the meal app, they see quick weeknight dinners and meal prep shortcuts. Retirees who sign up receive portion-controlled recipes and helpful tips for managing leftovers.
Facebook and Google ad campaigns work better with demographic filters. One campaign might target women aged 25-34 with messaging about “Meal prep that fits your busy life.” Another reaches families with “Feed everyone for under $50 a week.”
Automated email campaigns and other marketing messages should be segmented by demographic data. Different featured recipes go to different household sizes and age groups.
2. Psychographic segmentation

Source: https://www.joindrop.com/score-points/
Psychographic segmentation splits customers by values, interests, lifestyle, and motivations. This is where market research into customer preferences becomes valuable.
For instance, say you own a budgeting app, you could segment your audience based on motivations like becoming debt-free, building wealth, or saving for a rainy day.
Psychographic segmentation is one of the most effective customer segmentation models because demographics alone don’t explain motivation. Two 35-year-olds making $80K might use the budgeting app for entirely different reasons. One wants to pay off $30K in student loans. The other wants to save for a down payment on a house. Understanding these preferences helps marketers craft more relevant, personalized customer experiences.
How to do it
During onboarding, ask customers about their goals and values to better understand their needs. The budgeting app might ask a question like, “What’s your main financial goal?” with options such as “Pay off debt,” “Build wealth,” “Create emergency fund,” or “Track spending better.”
This single question assigns psychographic segments and shapes the entire customer journey.
MoEngage’s cross-channel marketing capabilities enable you to build seamless, contextual, and personalized customers journeys. Using this feature allows you to improve your customers’ journey and be better positioned to offer them products/services that they’ll be interested in.
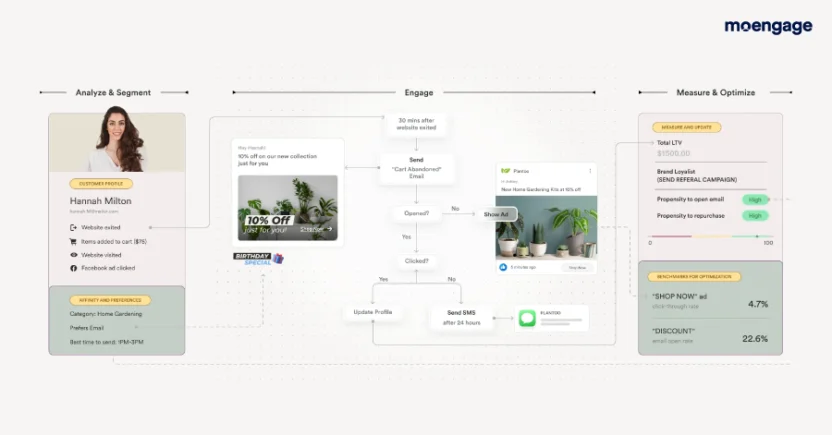
In-app behavior patterns reveal a lot about what drives different customers. So, track which features each segment uses most. Debt eliminators, for instance, might obsessively check their debt payoff timeline, while wealth builders pay more attention to investment tracking.
Use in-app messaging with psychographic targeting. When debt eliminators open the app, they might see something like, “You’re $847 closer to debt-free this month!” This personalization builds brand loyalty over time.
3. Behavioral segmentation
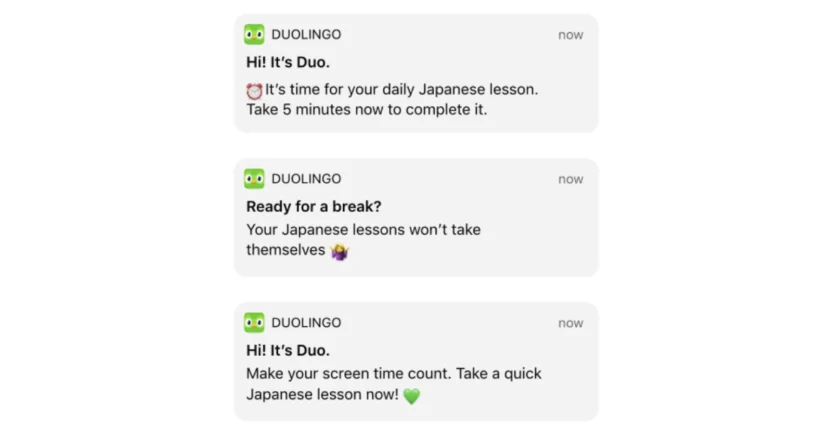
Source: https://blog.duolingo.com/content/images/2020/09/SM_090320-small.png
Another common customer segmentation model, behavioral segmentation groups customers by their actual actions: usage frequency, feature adoption, engagement level, and completion rates. This segmentation model relies heavily on customer data rather than assumptions.
A language learning app, for instance, could create segments like daily practitioners, consistent learners, weekend warriors, and inactive users.
Each group needs different marketing efforts and product experiences.
Behavioral segmentation is one of the most effective customer segmentation techniques because past behavior predicts future behavior more accurately than any other factor. Someone who’s completed 50 consecutive days will probably keep going. On the other hand, someone who’s skipped a week needs intervention to keep them from quitting.
How to do it
Analyzing performance across all customer touchpoints is the priority. Analytics tools should capture key actions, such as purchase frequency, feature usage, email engagement, website visits, login frequency, and the time since the last activity.
Behavioral segments need specific, measurable criteria. Vague labels like ‘engaged’ or ‘inactive’ don’t work. Instead, use precise definitions like “Purchased 3+ times in last 60 days,” “Opened last five emails but never clicked,” “Logged in 10+ times this month,”
or “No activity in 14+ days.” These clear definitions enable automated segmentation.
Your best customers share common behavioral patterns. So, monitor how your customers engage and nudge them towards successful behaviors.
Customers exhibiting early signs of churn require re-engagement emails and other marketing campaigns. First, define what ‘at risk’ looks like for your business. Then create a series of touchpoints to win them back. Test different approaches to determine what attracts inactive customers and fosters brand loyalty.
4. Geographic segmentation

Source: https://medium.com/@marketingoal/how-coca-cola-turns-heat-into-sales-marketing-examples-6d83e871b3cf
If demographic segmentation answers the question of who customers are, then geographical segmentation tells you where they are. As the name implies, here you group your audience based on their geographic location, from continent down to zip code.
However, this customer segmentation strategy often extends beyond simply knowing where your audience resides. It can also involve considering other factors, such as language, climate, workplace, and transportation.
This strategy is popular in the fashion industry, where clothing companies tailor their offerings to specific geographic regions. Thus, the same company might offer winter coats and boots in cold climates while offering hats and lightweight clothing in warmer areas.
Many marketers like to use this customer segmentation strategy mainly because of how easy it is to implement (home addresses and location data are easy to collect and analyze). Furthermore, collecting this type of data also typically provides insight into the demographic composition of the area, which is very useful for location-specific push notification campaigns.
How to do it
Location data should be collected at the time of sign-up. Ask for the ZIP code or city during the onboarding process. The metro area, time zone, and regional preferences are determined automatically from this information.
Analyze sales, engagement, or usage patterns by geography. Export your customer data by region and look for differences. Do certain locations prefer specific products? Do purchase frequencies vary by region? Does content engagement differ across markets?
Create location-based segments using criteria that are relevant to your business. Segment by climate if weather affects your product. Segment by urban versus rural if population density matters. Segment by region if cultural preferences vary. Segment by time zone if timing affects customer needs.
Customize your homepage, smart product recommendations, or featured content based on visitor location. Show region-relevant products, services, or information first. Expand to nearby areas only after showing what’s most immediately relevant. This segmentation marketing strategy improves the customer experience by reducing friction.
Adjust your email send times, promotional timing, or campaign scheduling to accommodate different time zones and local patterns. It wouldn’t be effective to send morning emails at 6 AM Pacific to East Coast customers who receive them at 9 AM. You should also consider regional shopping patterns, holidays, and cultural events when planning campaigns.
Test different offers, pricing, creatives or product bundles by geography if purchasing power or competitive dynamics vary by region. What works in high-cost urban markets may not be effective in rural areas.
5. Technographic segmentation
Technographic segmentation enables you to understand how customers behave based on their level of tech-savviness, software adoption patterns, and browsing habits. This, in turn, helps you optimize their experience.
Customers today buy and interact with products in ways that are distinct from how customers used to before, with traditional methods like television and radio.
As a customer segmentation example, a streaming service could segment its customers based on the device they use. The way they market to mobile-first customers would differ from how they market to smart TV users.
How to do it
Track device and platform data through your analytics. Capture information about the customer’s device type, operating system, browser, and the features they access on each platform.
Analyze feature usage by device type. For example, you could check if mobile users engage with different features than desktop users do. This information will spotlight behavior and reveal technology preferences.
Optimize your product experience for each technological segment. Because mobile-first users need thumb-friendly navigation and quick-loading pages, you’d need to follow mobile customer engagement strategies. Meanwhile, desktop users benefit from keyboard shortcuts and expanded views.
6. Needs-based segmentation
This customer segmentation model involves grouping customers by the specific problems they want to solve or goals they want to achieve.
It focuses on what your customers need from your product, rather than who they are or what they do.
This customer segmentation strategy is effective because it aligns your marketing and product development efforts with customer motivations. Two target markets might have similar demographics and behaviors, but completely different needs.
For example, a tour brand might target solo travelers who need budget travel itineraries as one audience segment, and couples that need luxury trips as another segment.
How to do it
Regularly conduct customer interviews and surveys, asking what problems your product solves and the main reason why customers use your product or service.
Keep the questions open-ended and look for common themes in the answers. Group similar needs together to identify your core need-based segments.
Another thing you can do is to analyze support tickets and customer service conversations. What questions do different customer groups ask? What features do they request? What frustrations do they express? These reveal unmet needs and help you understand what matters most to each segment.
Adjust your onboarding based on stated needs. When users sign up, ask about what brought them to your product and show relevant features first.
7. Value-based segmentation
Value-based segmentation is a customer segmentation model that splits customers by their actual or potential monetary value to your business.
To find a customer’s value, you could use metrics like customer lifetime value (CLV), purchase frequency, and average order value.
This segmentation strategy helps you allocate marketing efforts and resources where they’re most likely to generate the best return.
How to do it
Identify natural value tiers in your customer data. To do this, you need to calculate CLV. With that value, you can establish dollar thresholds that align with your business model.
Consider multiple value factors beyond revenue. Some customers spend less but refer others, which can lead to increased revenue. Some are low-maintenance and highly profitable. And still others might be early adopters who validate new features. All of these types of customers are important.
Adjust acquisition spend based on predicted customer value. If certain channels or campaigns attract high-value customers, invest more there even if the cost-per-acquisition is higher. It will do you well to focus on long-term value rather than just initial conversion costs.
How to Choose the Right Customer Segmentation Model for Your Business
Using customer segmentation models helps you engage directly with the customers who matter most to your brand. The right segmentation model ensures you’re grouping customers in ways that match their actual behaviors and tie directly to your marketing goals. The clearer you are on who you’re messaging and why, the easier it is to give them what they want.
Let’s break down the process of choosing the right model for your campaigns:
1. What is your overall marketing goal?
First things first, define clear goals and objectives for your marketing efforts. Determine whether you need to boost customer loyalty, increase brand awareness, enhance purchase frequency, encourage repeat purchases, or reduce customer churn.
That’ll help you figure out which customer segmentation model would be most suitable for adapting your marketing strategies to your customer segments.
For instance, if your goal is to increase your repeat purchase rate, consider examining buying frequency and loyalty program activity. To increase brand awareness, identify untapped audiences by focusing on specific demographic or geographic data.
Let’s say you’re trying to get more customers to use your shop locator. Using a customer segmentation strategy like behavioral segmentation, you can target customers who have downloaded your app and/or clicked on a specific ad.
With a clear goal and focused segmentation, you can ensure the segmentation model you select supports the goals and results you need.
2. Which customer personas engage with your brand the most?
Note the purchase or browsing behaviors and attributes of customer personas that interact with your brand. These may include their age range, lifestyle, shopping habits, and style preferences.
Then, analyze how different customer personas engage uniquely with your brand. For example, some personas may shop steadily all year, while others may buy only during seasonal sales. Then again, you’ll find personas who buy products due to an emotional connection, some who buy for utility, and others for maintaining a certain social status. All of these data points will help you categorize your customer personas into different segments.
Next, step into each segment’s shoes to figure out what problem they’re trying to solve, and what channels they’re using to interact with your brand.
The more you understand your customers and what makes them buy your products, the better you can grasp whether you need a demographic customer segmentation model, a behavioral one, or a mix of different models.
3. Do you have the tools to understand and act on your segments?
Your team should have the necessary tools to execute customer segmentation models, no matter which one you choose.
To assess whether your tools are powerful enough to do so, ask yourself:
- Can you monitor and analyze customer data accurately in real-time?
- Can you create segments that update based on changing customer behaviors?
- Can you deliver personalized automated marketing campaigns to these segments?
Was your answer “No” to all of these questions? In that case, you have two options: either invest in a tool that makes complex segmentation efficient, or select a simple segmentation model for now that your tool can easily execute.
8 Customer Segmentation Best Practices to Follow and Learn From
These practices are vital regardless of which segmentation strategy you use.
1. Have clear objectives
It’s essential to establish clear objectives even before deciding on a customer segmentation strategy.
Do you want to increase customer loyalty, refine your message, improve regional sales, or achieve something else?
Your goal will determine the best strategy to use. In fact, many companies have found that after defining the objectives they want to achieve, a combination of two or more methods has helped them to meet their objectives.
2. Define your segments
Vague or general categorization doesn’t help. Instead, create distinct segments with specific criteria. This could be based on any of the customer segmentation methods discussed earlier.
Clear definitions make segmentation actionable and scalable.
3. Build detailed customer profiles
Once you have defined customer segments, you can further refine your understanding by creating detailed customer profiles for each group or segment.
Document their behaviors, pain points, and aspirations. Include details you know about them and how they’ve interacted with your business.
These profiles help your entire team understand who they’re targeting and create more relevant marketing messages.
4. Get stakeholder buy-in
Your customer segmentation strategy might require input from multiple teams, vendors, contract employees (e.g, freelancers), customer service representatives, managers, and other stakeholders. This is because these stakeholders usually have incredible insight into what your customers want.
By including these stakeholders, not only will you obtain higher-quality data (which is critical to the success of your segmentation model), but you’ll also ensure that your model aligns with your company’s objectives.
5. Gather high-quality and comprehensive data
Accurate, current, high-quality, and comprehensive data have a positive impact on the quality and effectiveness of your customer segmentation strategy. With good data, you’ll be able to identify patterns and create accurate segments.
Depending on the strategy you choose, you can obtain this data from public records, such as census figures and national statistics websites.
However, you can also do data collection yourself via MoEngage’s survey tools. Other means of data collection include social listening and in-store traffic monitoring.
6. Follow the money
You might have discovered a large segment based on the data you’ve obtained and analyzed, but that segment isn’t instrumental if it doesn’t have purchasing power or if it doesn’t want or need your product.
Your customer segmentation strategy should prioritize profitability over segment size. You might discover a smaller segment with significant purchasing power and an interest in your product.
It’s best to focus on efforts in this segment regardless of its size.
7. Be adaptable
Adaptability is crucial as consumer behavior continues to evolve. Effective segmentation strategies require regular review and adjustment.
Remember that consumers and their circumstances are mutable, so while you might identify segments that don’t, at least for now, have the purchasing power or desire for your product, all of that might change tomorrow.
So, keep an eye on these segments as well, ready to scoop them up into your circle of purchasing customers.
8. Implement your segmentation plan
Before committing resources to your segments, validate that they’re distinct and actionable. You can achieve this by running A/B tests that compare segmented campaigns against generic ones.
Track key customer engagement metrics, including conversion rates, engagement, and LTV, by segment.
If two segments respond identically to different messaging, they may not be distinct enough.
When that happens, continue to monitor and refine your approach until you identify truly differentiated segments.
Perfect Your Customer Segmentation Strategy with MoEngage
You don’t need to use all four strategies at once for effective segmentation. Pick one segmentation model, get it working, then layer on another.
Start with the customer segmentation strategy that aligns best with your existing customer data and marketing efforts, then expand from there.
Book a demo to see how MoEngage can help you achieve your segmentation goals.
















