How to Build an Omnichannel Retail Strategy and Measure Its Success

Reading Time: 16 minutes
Let’s face it: customer attention is increasingly difficult to attract and retain in today’s digitized consumer climate. Modern retailers face the challenge of providing an optimized experience that keeps customers coming back.
To achieve the level of customer engagement they expect, retailers must leverage an omnichannel retail strategy. This strategy not only helps maximize engagement and drive retention but also plays a crucial role in offering a good omnichannel customer experience.
In this article, we’ll look at the concept of an omnichannel retail strategy, its core benefits, and how retailers can build an effective strategy. Additionally, we’ll explore the importance of measuring the success of your current customer engagement strategy and provide insights into the top metrics to use.
By understanding these metrics, retailers can optimize the performance of future campaigns and enhance the overall customer experience.
But first, what is an omnichannel retail strategy anyway?
What is an Omnichannel Retail Strategy?
An omnichannel retail strategy is a customer engagement strategy that uses interconnected, cross-channel communication to provide customers a seamless, familiar experience across all touch points. This customer-centric approach maximizes engagement, boosts retention, and increases conversions.
An omnichannel strategy helps marketers maximize the value of customer communication by ensuring all marketing and messaging works as part of a single, cohesive system. This empowers brands with deep insights and analytics that can power personalization efforts that allow them to connect with their audience and drive engagement.
6 Benefits of an Omnichannel Retail Strategy
The simple fact is, omnichannel marketing campaigns significantly outperform their single-channel counterparts. According to Forbes, omnichannel campaigns deliver customer engagement rates and conversion rates that are 250% higher than single-channel campaigns.
An effectively executed omnichannel strategy helps retailers increase conversions, average order values (AOV), customer lifetime value (LTV), and revenue.
Those who use an omnichannel strategy for retail marketing will see the following main benefits:
- Connect with customers where they are: By incorporating a variety of interconnected channels into your omnichannel strategy, you can reach customers wherever they are (at whatever time is most convenient).
- Remove barriers for customers: An omnichannel strategy helps retailers craft orchestrated journeys that seamlessly guide customers further down conversion funnels by removing unnecessary clicks and connecting with them over the right channel at the right time.
- Helps teams deliver personalized campaigns: An omnichannel strategy allows retailers to deliver their customers targeted, hyper-personalized content and messaging that resonates with them.
- Maximize customer engagement: More than anything, an omnichannel strategy drastically increases engagement by providing customers an intuitive, seamless, integrated, customer-centric experience.
- Increase conversion rates: Optimized omnichannel campaigns that connect with customers via the optimal channel garner higher open rates and achieve greater impact and are therefore, far more likely to lead to a conversion.
- Improve retention and stickiness: An optimal experience keeps customers interested and motivates them to return to make repeat purchases. Over time, this allows retailers to increase average order value (AOV), customer lifetime value (LTV), and overall revenue.
- Foster deep brand loyalty: Customers who receive a familiar, seamless experience whenever they access your brand will return for more. The right messaging on the right channel allows brands to build meaningful relationships with customers that lead to not just loyalty, but brand advocacy.
- Drive word-of-mouth marketing: Customers remember their best experiences (and share them with friends). A best-in-class customer experience is highly sought after, and loyal customers are likely to advocate for your brand (and gain new visitors).
- Obtain valuable customer insights: An omnichannel system allows you to collect and unify customer data, providing retailers a holistic view of their customers that empowers them to conduct deep customer analysis that leads to meaningful, actionable insights. Omnichannel analytics then informs future campaigns, allowing retailers to create a cyclical loop where campaigns are optimized with each reiteration.
An omnichannel strategy is a must-have for retailers looking to drive customer engagement and propel them toward their goals of increased conversions, average order value, and customer lifetime value.
How to Build Your Omnichannel Retail Strategy
Customer acquisition, retention, and loyalty don’t just happen overnight, they take precise planning and perfectly executed marketing campaigns that customers resonate with and want more of. To do this properly, retailers need a finely crafted omnichannel strategy to propel them to success by maximizing engagement.
Below, we look at how retailers can build an effective omnichannel retail marketing strategy that drives customer engagement and leads to deep brand loyalty.
1. Segment customers into buyer personas
Being able to communicate via your customers’ preferred channels doesn’t magically happen, it requires serious planning and needs to be based on accurate, reliable data.
Customer segmentation and cohort analysis enable retailers to maximize the impact of omnichannel campaigns by ensuring brands reach out to customers via the best channel (at the right time).
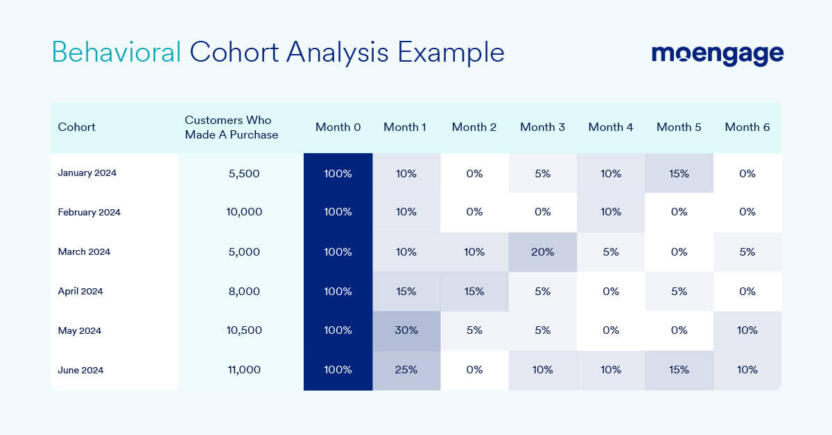
Segment customers based on age, gender, geographic location, and even behavioral patterns to help you improve your marketing efforts and maximize customer engagement. Use this data to build buyer personas for your various customer types that will inform how you map customer journeys, what channels you use, and how you craft individual campaigns to get the best results.
By ensuring your omnichannel retail strategy is data-driven, you can make more informed, meaningful, and impactful decisions when building your overall strategy and individual campaigns.
2. Select your priority channels
After you’ve considered who your customers are and how they’ll interact with your brand, it’s time to choose the channels you’ll use for your omnichannel strategy.
Beyond simply selecting the channels themselves, you’ll want to consider how you’ll leverage these channels for best results with your visitors. What channels do you use for different types of messages? Which channels are best for specific customer segments and cohorts? Think critically about not just what’s convenient for you to manage, but what’s ideal from your customers’ perspective.
Keep in mind that you aren’t limited to these channels, you can always integrate additional channels into your omnichannel strategy or remove ones that are underperforming. The key is to test and analyze campaigns so you understand what is (and isn’t) working, helping you identify where your biggest strengths and weaknesses are. Once you’ve identified the areas of improvement, you can begin to optimize your strategy by leveraging the right channels for your audience.
3. Anticipate and map customer journeys
Now that you understand who your customers are and what channels they prefer, you can begin to map out what customer journeys look like.
Orchestrate customer journeys that leverage all the channels at your disposal and trigger at the right times for optimal engagement. Determine at what points in the customer journey you plan to deploy messaging and identify which channels you’ll use at each stage in the process. Fine-tune these journeys to better guide customers through conversion funnels so they opt-in to notifications, add items to their cart, complete checkout, and return to buy more!
4. Streamline and unify your channels
Now that you know the channels you’ll use for your campaigns and at which point in the customer journey you’ll deploy them, you can begin to unify, streamline, and optimize your omnichannel strategy.
Make sure all the moving parts — channels, content, and timing — work together to create the best customer experience possible and pull customers down optimized pathways that increase satisfaction and foster brand loyalty. The result should be an omnichannel strategy that leverages all of your interconnected channels as part of a single, cohesive system designed to maximize customer engagement.
The end result should be an omnichannel strategy that uses fully integrated channels to provide a seamless, familiar customer experience across all channels. This not only means intertwining all digital channels, but also bridging the gap between digital and in-store channels.
For example, leading brands like The Home Depot and Sephora have capitalized on the fact that 80% of customers use their mobile phones while shopping at a physical location by leveraging their mobile app to supplement the in-store shopping experience.
5. Respond dynamically to insights and analytics
Marketing campaigns are never “set it and forget it” situations and — unfortunately — no omnichannel strategy lasts forever. Just as your customers’ shopping habits evolve, your omnichannel strategy will need to adapt to keep up with their changing needs.
Retailers will need to regularly review the performance of their omnichannel retail strategy and make improvements that are rooted in data and analytics to make sure they are developing campaigns and experiences that resonate with their customers. Use customer engagement data to identify what is and isn’t working, and then fine-tune your strategy to leverage the right channels for the right customers (and the right messages).
Make sure your overall strategy and individual campaigns are informed by accurate, reliable data that paints a clear picture of your customers, factoring in their preferences, interests, and behavior. Analyze KPIs to get an idea of how you are performing and to identify areas of improvement. A/B test your campaigns to truly understand what is and isn’t working, and then adjust accordingly to improve your strategy and optimize your campaigns to maximize performance.
5 Examples of Omnichannel Strategies of Top Retailers
Now that you know how to build and manage your omnichannel strategy, it’s time to execute it in practice. Unfortunately, knowing how to execute your strategy and actually executing it are two very different things.
To help you bring your strategy to life, we cover concrete, real-life examples of how leading retailers have made omnichannel retail strategies work for them, helping them increase engagement and retention.
1. Old Navy uses an omnichannel experience to effectively cross-sell

An omnichannel strategy provides a seamless customer experience by ensuring that data is collected from and leveraged across all channels simultaneously and in real time. This allows retailers to offer personalized product recommendations, even after customers shop via a different channel.
Despite the fact that this customer commonly does their browsing on mobile, they typically finish their shopping and complete their purchase via the website. Old Navy’s omnichannel strategy ensures that the user experience is exactly the same on desktop as it is on mobile, factoring in the customer’s recent activity and applying it to their current shopping experience.
This allows Old Navy to deliver hyper-personalized product recommendations that are far more likely to end in a successful cross-sell or upsell opportunity.
2. Google Play alerts customers of price drops with perfectly timed mobile push notifications
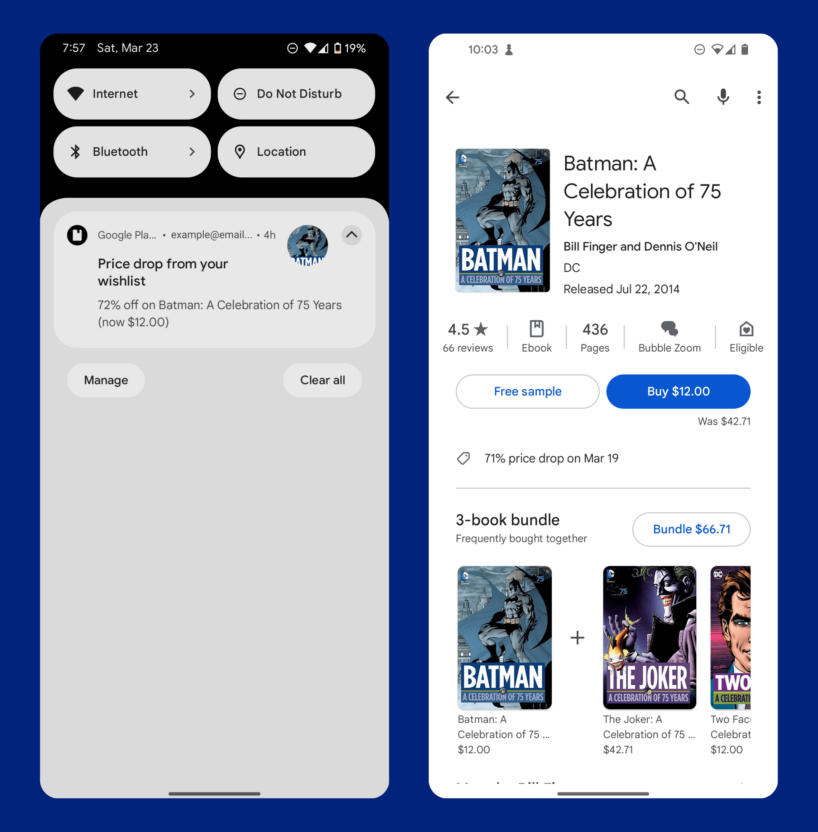
Though push notifications have the opt-in barrier with customers, once activated, they are a reliable way to keep your brand top of mind and keep customers engaged.
A great retail example is Google Play Books using push notifications to serve targeted discounts and promote a product that the customer has previously added to their wishlist (and are clearly interested in). Whether they added this to their wishlist in-app or on the web, an omnichannel strategy allows Google Play to connect with the customer via any integrated channel. In this example of personalized media marketing, they use a mobile push notification to alert the customer of the offer so that the customer is sure to get the message and won’t miss out on the offer.
Customers are frustrated when they are offered items that don’t apply to them. A targeted discount for something already on the customer’s wishlist, or that they’ve clearly been considering (clicking on the page more than one time), proves much more satisfying, drastically increasing engagement and conversions.
3. McDonald’s gains traction with orchestrated customer onboarding journeys
A new customer is a repeat customer waiting to happen. Newly onboarded customers must be treated with care to extend their potential. The lifetime value of any one of your customers relies on the brand’s attention to detail.

McDonald’s leverages an omnichannel strategy to onboard customers to their MyRewards program by crafting orchestrated journeys that engage with customers via their mobile app, email, and mobile push. The entire sequence ensures that they welcome the new member, explain how the program works, and encourage the customer to participate in MyRewards actively.
This includes an informative sequence explaining how the rewards work and how the app can collect and use points. This email lets the new member know they have a welcome offer, followed by a mobile push that reminds them of this limited-time offer as it expires.
This entire omnichannel, orchestrated journey is crafted to onboard customers to the MyRewards program and encourage them to actively participate, fostering customer engagement and building long-term loyalty.
The campaign is informational, engaging, and rewarding to the customer. What more could they ask for?
4. H&M promotes limited-time sales with an omnichannel sequence
H&M uses an omnichannel communication strategy that leverages email and mobile push notifications to promote a limited-time sale and encourage customers to shop online and in-store.
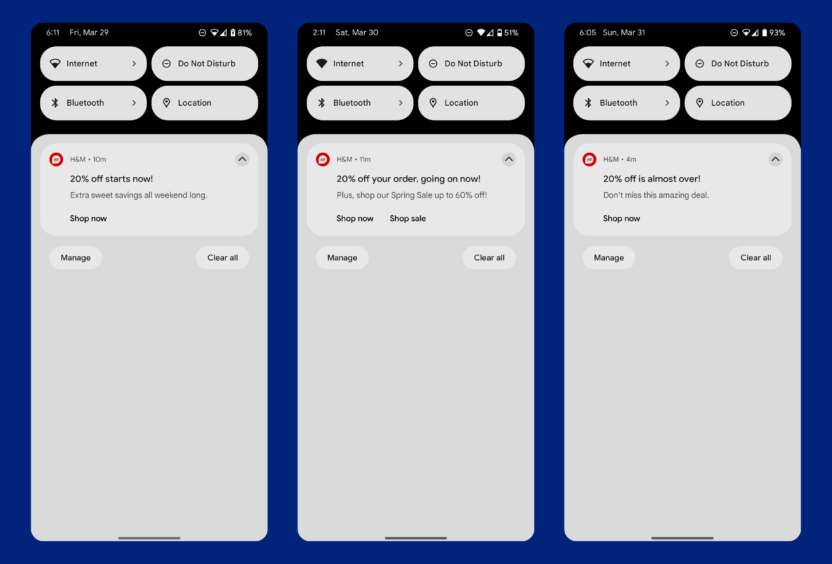
Email promotes the sale weeks in advance, showcasing featured products and advertising when the sale will be. This makes customers aware of the sale, but allows them to interact at a most convenient time.
As we get closer to the time of the sale, mobile push notifications are used to drive urgency and ensure customers actually get the message. The weekend of the sale, a mobile push sequence is triggered that sends 3 crafted messages, one for each day of the weekend, that ensure customers don’t miss out on the sale. Carefully timed and worded messaging curates a seamless sequence that encourages both online and offline engagement, driving customers where you want them to be.
This is the perfect execution of an omnichannel strategy, combining specific channels, carefully crafted messaging, and perfectly timed delivery to optimize the customer experience and maximize engagement. Here, H&M uses an omnichannel strategy to orchestrate a marketing campaign that encourages customers to engage with the limited-time sale, getting them to buy both online and in-store.
5. Walmart uses personalized omnichannel sequences to get customers online and in-store
When leveraged effectively, an omnichannel strategy allows retailers to deploy hyper-personalized and highly orchestrated customer experiences that drive engagement, conversions, and customer satisfaction.
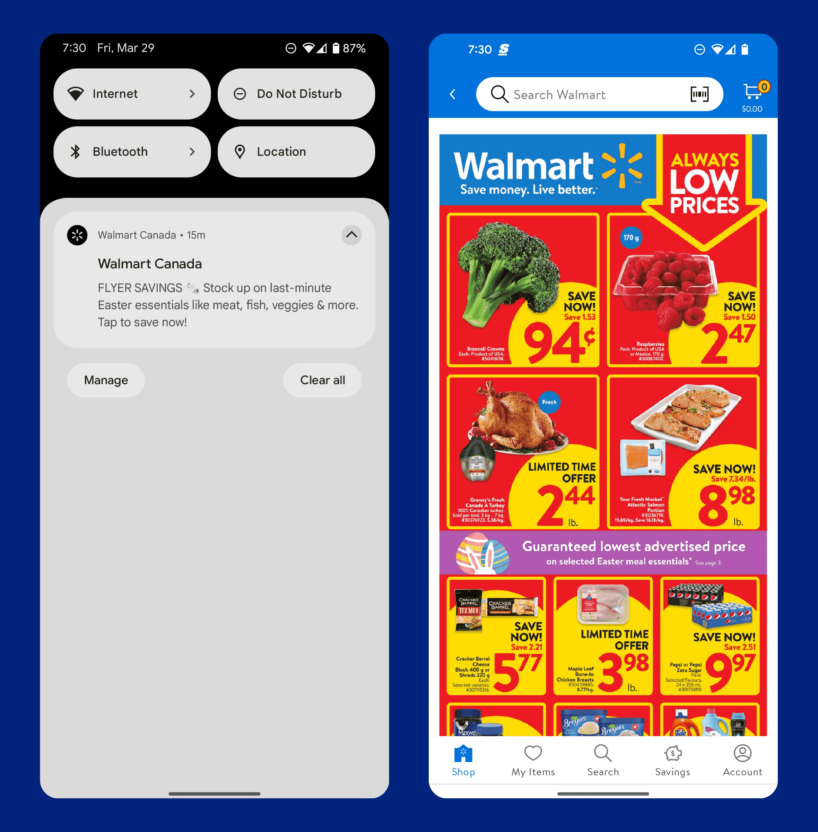
Walmart uses an orchestrated omnichannel sequence to drive engagement with the active weekly sale. First, a mobile push notifies the customer about the sale. When clicked, this brings the customer into a curated in-app experience that connects shoppers with the most current local flyer using geographic location data.
This streamlined experience creates a fast, efficient journey that alerts customers of their local sale and encourages active engagement. Shoppers can immediately place an order online or use the digital flyer to support their in-store shopping experience.
Regardless of how the customer chooses to shop, this is a simple example of how H&M uses omnichannel communication to funnel customers towards a conversion event, in this case driving customers to shop online or in-store.
How to Analyze the Success of Your Omnichannel Retail Strategy
A stagnant strategy will never succeed in a swiftly shifting retail and ecommerce environment. For retailers to stay ahead of their competition, they’ll need to regularly analyze their performance and make improvements that customers love.
For brands to make informed, data-driven decisions, they need to cement these decisions on accurate, reliable data. But before that, they need to make sure the KPIs they use to inform these decisions are the right ones for measuring success and identifying shortcomings at various points in the customer lifecycle.
To help retailers maximize engagement with an omnichannel strategy, we look at the metrics they can use to measure success at various points in the customer lifecycle and across their channelsthe various channels they’re using.
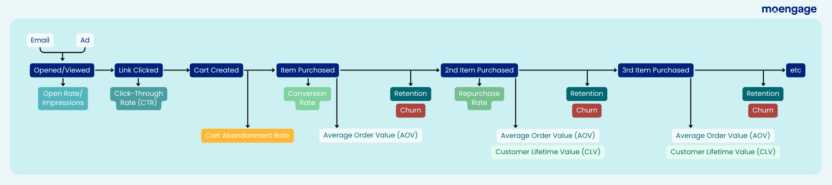
While these metrics can’t tell you exactly what your customer engagement problem is or how to fix it, they can help you identify where your biggest weaknesses are so you can analyze further and make meaningful improvements.
By leveraging the following metrics, you can get a baseline for how your omnichannel retail strategy is performing, and be able to optimize your campaigns to achieve peak performance.
1. Open Rates

The open rate indicates the percentage of sent messages that are opened by the recipient.
Even the most well-crafted marketing messages won’t be successful if your customers never see them. Open rates are a solid indicator of which channels are drawing — and capturing — customer attention. Use open rate data to help you choose the channels you use as part of your campaigns.
Emails have notoriously low open rates, so you’ll want to do everything you can to test different subject lines and dynamic content to get the most out of your emails. SMS messages have strikingly high open rates, so you’ll want to ensure you’ve crafted eloquent messaging that customers resonate (and engage) with.
Be strategic about the messaging you use for different channels to maximize engagement. Leverage SMS for time-sensitive, direct messages and emails for brand announcements, account updates, and more generic offers.
2. Click-Through Rate (CTR)
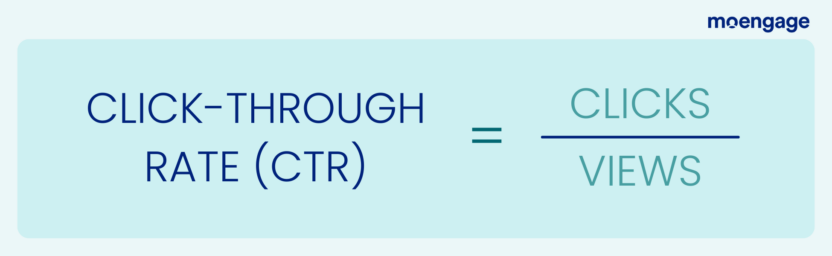
The click-through rate (CTR) indicates how many customers click a product recommendation, promotional offer, or other embedded link after opening or viewing a message.
For retailers, the CTR is a good indicator of how well their marketing messages capture qualified leads. This metric can be used to analyze the performance of your website, emails, SMS messages, mobile push notifications, and pretty much any other digital channel you operate.
When analyzed properly, CTR helps retailers identify underperforming campaigns, singling out subject lines, message copy text, and dynamic content that isn’t working well so it can be improved to increase traction. CTR can also identify which channels garner the most engagement, allowing you to isolate which channels need improvement and reassess your priorities.
3. Cart Abandonment Rate

The cart abandonment rate indicates how many customers leave a shopping session without purchasing after adding an item to their cart.
More than anything, retailers use this metric to highlight potential issues with their checkout process. After all, if customers are abandoning items after adding them to their cart, they likely ran into a problem while checking out. An issue with your checkout can significantly impact conversions and needs to be immediately assessed and optimized, no matter the channel.
For omnichannel retailers, the cart abandonment rate provides insights into which channels have the best-performing checkout processes and experiences. Brands can then identify which channels are struggling, determine the problem, and work on a fix for that specific channel. Overall, this allows teams to identify and remove barriers for different channels to build streamlined, orchestrated journeys that save customers time — and increase conversion rates.
It also gives retailers an avenue to recover abandoned customers by triggering cart abandonment and customer recovery campaigns.
4. Conversion Rate

The conversion rate represents the percentage of visitors that complete a conversion event.
One of the most vital metrics for retailers, the conversion rate is a direct indicator of how well your conversion funnels are performing. In the most basic sense, it tells you how effective your brand is at getting customers to perform a conversion event, whether that’s an opt-in, a sign up, or an actual purchase.
While most companies use this as their most important KPI and the greatest indicator of their success, there is far more to consider regarding long-term brand success. Conversion rates are a great indicator of lead generation and customer acquisition, but retention and brand loyalty are built over time and require customers to make repeat purchases.
For omnichannel retailers, the conversion rate can be used to compare the performance of different channels and individual campaigns. This allows you to hone in on the fine details that lead to (or cost you) a sale. It also, allows you to refine your customer journeys and better guide customers towards repeat purchases, increased order values, and true brand loyalty.
5. Average Order Value (AOV)

Average order value (AOV) indicates the average value of a single order.
Retailers can use this as a baseline indicator of a brand’s success. More particularly, it’s a strong indicator of a retailer is effectiveness at upselling and cross-selling to their customers.
By comparing AOV across your operating channels, you can get a good picture of which channels are performing best overall. More than that, by examining the AOV of individual campaigns, you can understand which campaigns are doing the best job of increasing AOV, and then use that to optimize your customer journeys to perform even better.
6. Repurchase Rate
![The formula for calculating repurchase rate]](https://www.moengage.com/wp-content/uploads/repurchase-rate-formula-1-832x256.png)
The repurchase rate represents the percentage of visitors who make more than one purchase.
For retailers, it’s a strong measure of customer satisfaction, and can even be an early indicator of future retention rates and brand loyalty. After all, if the customer returned to make a second purchase, they were satisfied with either the product or experience.
In an omnichannel retail strategy, a repurchase rate is a solid indicator of how well your omnichannel strategy works, how seamless the customer experience is, and how well your marketing campaigns are performing. Beyond this, it’s a strong signal of your customer retention. If you can capitalize on this customer satisfaction, you can use your omnichannel strategy to further connect with customers and build loyalty.
7. Customer Retention Rate

The customer retention rate represents the number of customers that remain after a specified period of time.
While most retailers treat their conversion rate as their most important metric, customer retention is a far more important factor than customer acquisition when it comes to the long-term success of a brand. It’s not only a great indicator of the success of your omnichannel strategy, but also the performance of individual campaigns. Again, comparing the retention metrics across different channels and campaigns is a great way of measuring their overall performance. Most importantly, retention is a strong signal for positive customer engagement, far stronger than a single conversion.
It’s also an early signal for long-term brand success and deep customer loyalty that will last (and lead to greater AOV and LTV).
8. Churn Rate

The inverse of the customer retention rate, the churn rate represents the number of customers lost during a specified period of time.
This is a vital metric for understanding customer retention. While the customer retention rate is often used to identify channels, strategies, and campaigns performing well, the churn is often used to identify (and analyze) those underperforming. Churn is often applied to individual campaigns, allowing teams to identify which channels and messages in an orchestrated journey fail to connect with customers (and garner the expected engagement).
High churn rates are solid indicators of where customers are dropping off throughout the customer journey, allowing you to identify which processes need the most attention.
9. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) or (LTV)

Customer lifetime value (CLV), sometimes called customer LTV, indicates the average value each customer brings to your brand over their lifetime as your customer.
Retailers use this as a baseline to measure marketing success, understand brand growth, cross-selling effectiveness, and, most significantly, customer retention. After all, a higher CLV shows you’ve successfully improved customer retention by increasing one of the following: click-through rates, repurchase rates, average order values, or all three.
Customer lifetime value is a vital metric for determining how valuable a customer acquisition is to your brand. It also allows you to conduct a cost-benefit analysis on the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns, which can be used to justify funding and budget allocation.
Comparing CLV across your channels helps you identify which channels bring the most value to your brand. By comparing the performance of individual campaigns, you can improve your messaging to gain traction and increase engagement.
Carry Out Comprehensive Omnichannel Retail Strategies With MoEngage
An omnichannel strategy is essential for maximizing customer engagement with modern shoppers. It enables physical and digital retailers to connect with their customers with the right messaging at the right time and via their preferred channels. This customer-centric approach drastically improves customer experience — and satisfaction — ensuring your customers return for more.
As our examples of real-life, leading retail brands have proven, when done right, an omnichannel strategy empowers brands to craft complex, orchestrated journeys that nurture leads and guide customers toward conversion events.
Here at MoEngage, we help brands build omnichannel retail strategies that their customers resonate with so they don’t just increase conversions but instead foster deep, long-lasting brand loyalty that leads to higher average order values (AOV), customer lifetime value (CLV), and revenue.
Schedule a demo today to learn how MoEngage can power an omnichannel strategy that delivers hyper-personalized, perfectly timed messages to your customers that get real results.